Abstract
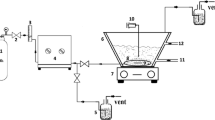
Degradation of 4-chloro-2-nitro phenol by ozonation in aqueous solution was studied in a semi batch reactor under constant ozone dosage and variable pH conditions. The effectiveness of the process was estimated based on the degree of conversion of 4-chloro-2-nitro phenol. It was observed that ozonation is more effective at alkaline reaction of medium than other conditions. The degree of conversion achieved (at the first 5 minutes of the process)at pH 9 was 99.64% compared to 99.03% and 77.35% at pH 7 and 3, respectively. Another parameter used to quantify the 4-chloro-2-nitrophenol during ozonation was the pseudo first order rate constant k [min−1]. Results showed that the rate constant of the process was approximately much higher at the alkaline pH compared to acidic ones. A considerable improvement in chemical oxygen demand removal was observed at pH above 7. At pH 9, the reduction in chemical oxygen demand at the end of the process reached 56.9 %. The degree of organically bounded nitrogen conversion to nitrate was higher at pH 3. Of the total organic carbon reduction, 15.89 % was observed at pH 9. The 4-chloro-2-nitro phenol degradation intermediate products were analyzed by mass- spectrometry. The main intermediate product was chlorophenol.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alaton, I. A.; Balcioglu, I. A., (2001). Photochemical and heterogeneous photocatalytic degradation of waste vinyl sulphone dyes: A case study with hydrolyzed Reactive Black 5. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A, 141 (2-3), 247–254 (8 pages).
Andrews, S. A.; Huck, P. M.; Coutts, R. T., (1993). Quantitation of ozonation by-products of fractionated aquatic natural organic matter. Worn. Wasser., 81 (2), 151–165 (15 pages).
Beltran, F. J.; Encinar, J. M.; Alonso, M. A., (1998). Nitroaromatic hydrocarbon ozonationin water. 1. Single ozonation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 37 (1), 25–31 (7 pages).
Benitez, F. J., (2003). Ozone reaction kinetics for water and wastewater systems, 1st. Ed. Lewis Publishers, 124.
Benitez, F. J.; Beltran-Heredia, J.; Acero, J. L.; Rubio, F. J., (2000). Rate constants for the reactions of ozone with chlorophenols in aqueous solutions. J. Hazard. Mater. B, 79 (3), 271–285 (15 pages).
Chu, W.; Wong, C. C., (2003). A disappearance model for the prediction of trichlorophenol ozonation. Chemosphere, 51 (4), 289–294 (6 pages).
Diwani, G. E.; Rafie, S. E.; Hawash, S., (2009). Degradation of 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene in aqueous solution by ozonation and multi-stage ozonation biological treatment. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 64, 619–628 (10 pages).
Gharbani, P.; Tabatabaii, S. M.; Mehrizad, A., (2008). Removal of Congo red from textile wastewater by ozonation. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 5 (4), 495–500 (6 pages).
Giri, R. R.; Ozaki, H.; Taniguchi, S.; Takanami, R., (2008). Photocatalytic ozonation of 2, 4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid in water with a new TiO2 fiber. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 5 (1), 17–26(10 pages).
Goi, A.; Trapido, M.; Tuhkanen, T., (2004). A study of toxicity, biodegradability and some by-products of ozonised nitrophenols. Ad. Environ. Res., 8 (3-4), 303–311(9 pages).
Graham, N.; Chu, W.; Lau, C., (2003). Observations of 2, 4, 6-trichlorophenol degradation by Ozone. Chemosphere, 51 (4), 237–243 (7 pages).
Gunten, U. V.; (2003). Ozonation of drinking water. Part 1. Oxidation kinetics and product formation. Water. Res., 37 (7), 1443–1467(25 pages).
Gurol, M. D.; Vatistas, R., (1987). Oxidation of phenolic compounds by ozone and ozone + UV radiation: A comparative study. Water Res., 21 (8), 895–900 (6 pages).
Hoigne, J., (1998). Chemistry of aqueous ozone and transformation of pollutants by ozonation and advanced oxidation processes, in: Hrubec, J. (Eds.), The Handbook of Environ. Chem. Springer-Verlag., Berlin.
Hoigne, J.; Bader, H., (1983). Rate constants of reactions of ozone with organic and inorganic compounds in water I. Water Res., 17 (2), 173–183 (11 pages).
Hong, P. K. A.; Zeng, Y., (2002). Degradation of pentachlorophenol by ozonation and biodegradability of intermediates. Water Res., 36 (17), 4243–4254 (12 pages).
Huang, W. H.; Fang, G. G.; Wang, C. C., (2005). A nanometer-ZnO catalyst to enhance the ozonation of 2,4,6-trichlorophenol in water. Colloids Surf. A, 260 (1), 45–51 (7 pages).
Kasprzyk-Hordern, B.; Ziolek, M.; Nawrocki, J., (2003). Catalytic ozonation and methods of enhancing molecular ozone reactions in water treatment. Appl. Catal. B: Environ., 46 (4), 639–669 (31 pages).
Kuo, C. H.; Huang, C. H., (1995). Aqueous phase ozonation of chlorophenols. J. Hazard. Mater., 41 (1), 31–45 (15 pages).
Legube, B.; Karpel, N. V. L., (1999). Catalytic ozonation: a promising advanced oxidation technology for water treatment. Catal. Today, 53 (1), 61–72 (12 pages).
Legube, B.; Langlais, B.; Sohm, B.; Dor, M., (1981). Identification of ozonation by-products of aromatic hydrocarbon micropollutants: Effect on chlorination and biological filtration. Ozone Sci. Eng., 3 (1), 33–48 (16 pages).
Madukasi, E. I.; Dai, X.; He, C.; Zhou, J., (2010). Potentials of phototrophic bacteria in treating pharmaceutical wastewater. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 7 (1), 165–174 (10 pages).
Muthukumar, M.; Sargunamani, D.; Selvakumar, N.; Rao, V. J., (2004). Optimization of ozone treatment for color and COD removal of acid dye effluent using central composite design experiment. Dyes Pigments, 63 (2), 127–134 (8 pages).
Panjeshahi, M.H.; Ataei, A., (2008). Application of an environmentally optimum cooling water system design in water and energy conservation. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 5(2), 251–262 (12 pages).
Samarghandi, M. R.; Nouri, J.; Mesdaghinia, A. R.; Mahvi, A. H.; Nasseri, S.; Vaezi, F., (2007). Efficiency removal of phenol, lead and cadmium by means of UV/TiO2/H2O2 processes. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 4 (1), 19–25 (7 pages).
Sarasa, J.; Roche, M. P.; Ormad, M. P.; Gimeno, E.; Puig, A.; Ovelleiro, J. L., (1998). Treatment of a wastewater resulting from dyes manufacturing with ozone and chemical coagulation. Water Res., 32 (9), 2721–2727 (7 pages).
Saritha, P.; Aparana, C.; Himabindu, V.; Anjaneyulu, Y., (2007). Advanced oxidation of 4-chloro-2-nitrophenol (4C-2NP) — A comparative study. J. Hazard. Mater., 149 (3), 609–614 (6 pages).
Sauleda, R.; Brillas, E., (2001). Mineralization of aniline and 4-chlorophenol in acidic solution by ozonation catalyzed with Fe2+ and UVA light. Appl. Catal. B: Environ., 29 (2), 135–145 (11 pages).
Shen, J. M.; Chen, Z. L.; Xu, Z. Z.; Li, X. Y.; Xu, B. B.; Qi, F., (2008). Kinetics and mechanism of degradation of p-chloronitrobenzene in water by ozonation. J. Hazard. Mater., 152 (3), 1325–1331 (7 pages).
Song, S.; Xia, M.; He, Z.; Ying, H.; Lu, B.; Chen, J., (2007). Degradation of p-nitrotoluene in aqueous solution by ozonation combined with sonolysis. J. Hazard. Mater., 144 (1-2), 532–537 (6 pages).
Stockinger, H.; Heinzle, E.; Kut, O. M., (1995). Removal of chloro and nitro aromatic wastewater pollutants by ozonation and biotreatment. Environ. Sci. Tech., 29 (8), 2016–2022 (7 pages).
Utsumi, H.; Han, Y. H.; Ichikawa, K., (2003). A kinetic study of 3-chlorophenol enhanced hydroxyl radical generation during ozonation. Water Res., 37 (20), 4924–4928 (5 pages).
Villaseñor, J.; Reyes, P.; Pecchi, G., (2002). Catalytic and photocatalytic ozonation of phenol on MnO2 supported catalysts. Catal. Today, 76 (2), 121–131(11 pages).
Wu, J.; Rudya, K.; Sparka, J., (2000). Oxidation of aqueous phenol by ozone and peroxidase. Adv. Environ. Res., 4 (4), 339–346 (8 pages).
Zareen, K.; Anjaneyulu, Y., (2005). Influence of soil components on adsorption —desorption of hazardous organic-development of low cost technology for reclamation of hazardous waste dumpsites. J. Hazard. Mater. B, 118 (1-3), 161–169 (9 pages).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gharbani, P., Khosravi, M., Tabatabaii, S.M. et al. Degradation of trace aqueous 4-chloro-2-nitrophenol occurring in pharmaceutical industrial wastewater by ozone. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 7, 377–384 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03326147
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03326147