Abstract
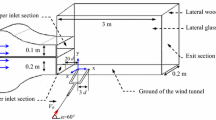
The choking of dual subsonic streams flowing through a convergent duct in contact has been investigated experimentally and theoretically. The experiment was conducted by using blow-down wind tunnel. The condition, when the dual stream flow choking (compound choking) occurs at the nozzle exit, was explained by one-dimensional analysis of compound sound wave propagation. The experimental results for the condition of compound choking were compared with the prediction from theoretical analysis, and the schlieren optical method using the spark light source has been used to visualize the flowfield.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A i :
-
Stream cross sectional area, i=1, 2
- a :
-
Speed of sound
- C i :
-
Propagation velocity of compound sound wave, i=1, 2
- P e :
-
Static pressure of duct exit
- P oi :
-
Plenum chamber pressure, i=1, 2
- a :
-
Absolute propagation velocity of compound sound wave
- γ i :
-
Ratio of specific heats, i=1, 2
- ϕ:
-
Plenum chamber pressure ratio (=p 02/p 01) Subscripts
- 1:
-
High speed subsonic stream
- 2:
-
Low speed subsonic stream
References
Bernstein, A. et. al., 1967, “Compound-Compressible Nozzle Flow,”Trans, of the ASME, J. Applied Mechanics, pp. 548–554.
Clark, L. T., 1995, “Application of Compound Flow Analysis To Supersonic Ejector-Mixer Performance Prediction,”AIAA Paper, 95–0645.
Fage, E., 1976, “Apparent Subsonic Choking in Dual-Stream Nozzles,”AIAA J., 14–5, pp. 681–683.
German, R. C. et. al., 1966, “Methods for Determining the Performance of Ejector- Diffuser Systems,”J. Spacecraft, 3-2, pp. 193–200.
Hoge, H. J., and Segars, R. A., 1965, “Choked Flow: A Generalization of the Concept and Some Experimental Data,”AIAA J., 3–12, pp. 2177–2183.
Lewis, M. J. and Hastings. D. E., 1987, “The Influence of Flow Non-Uniformities in Air-Breathing Hypersonic Propulsion Systems,”AIAA J.,. 87–2079, pp. 1–14.
Pearson, H., et. al, 1958, “The Theory of the Cylindrical Ejector Supersonic Propelling Nozzle,”J. Royal Aeronautical Society, 62, pp. 746–751.
Schindel, L., 1999, “Effect of Nonuniform Nozzle Flow on Scramjet Performance,”J. Propulsion and Power, 15–2, pp. 363–364.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kwon, JK., Masusaka, K., Miyazato, Y. et al. Compound choking of a two-parallel stream through a convergent duct. KSME International Journal 15, 1829–1834 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03185141
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03185141