Summary
-
1.
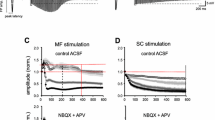
In rabbits and cats anaesthetized by urethane-chloralose or pentobarbital sodium, stimulation of the commissural afferent pathway produced a negative field potential with maximal amplitude in the CA3 basal dendritic layer, and with a latency indicative of monosynaptic activation of excitatory synapses on the basal dendrites.
-
2.
Mossy fibre stimulation resulted in a similar field potential restricted to the mossy fibre layer. Comparable negative field potentials were found in the layer of apical dendrites in CA1 in response to commissural and Schaffer collateral stimulation, suggesting a dendritic location of these synapses.
-
3.
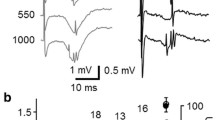
All negative field potentials grew in amplitude on tetanic stimulation, to produce large extracellular spikes, indicating their association with excitatory synaptic activity.
-
4.
Usually, all pathways employed failed to produce EPSPs on single shock stimulation, in spite of their capability of discharging the cells, suggesting that the synaptic depolarization takes place at some distance from the soma.
-
5.
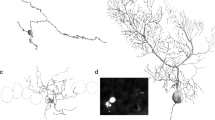
Electron microscopy of degenerated commissural afferent fibres showed them to make contact with spines or the smooth surface of thin dendrites. The indentification of the postsynaptic element as pyramidal cell dendrite was ascertained. The mossy fibres end on ramified dendritic spines in CA3.
-
6.
By comparison with normal electron micrographs, all the pathways, shown physiologically to be excitatory, terminate on thin dendrites, the contacts being of type 1.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alksne, J.F., T.W. Blackstad, F. walberg and L.E. White Jr.: Electron microscopy of axon degeneration: a valuable tool in experimental neuroanatomy. Ergebnisse der Anat. Entw. gesch. 39, 3–31 (1965).
Andersen, P.: Interhippocampal impulses. II. Apical dendritic activation of CA1 neurons. Acta physiol. scand. 48, 178–208 (1960).
—, J.C. Eccles and Y. Löyning: Recurrent inhibition in the hippocampus with identification of the inhibitory cell and its synapses. Nature (Lond.). 198, 540–542 (1963).
—: Location of postsynaptic inhibitory synapses on hippocampal pyramids. J. Neurophysiol. 27, 592–607 (1964).
— and P.E. Voorhoeve: Postsynaptic inhibition of cerebellar Purkinje cells. J. Neurophysiol. 27, 1138–1153 (1964).
-, B. Holmqvist and P.E. Voorhoeve: Excitatory synapses on hippocampal apical dendrites activated by entorhinal stimulation. Acta physiol. scand. (1966). In press.
Andersen, P., and T. Lömo: Excitation of hippocampal pyramidal cells by dendritic synapses. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 181, 39–40 P (1965).
Araki, T., and T. Otani: Response of single motoneurones to direct stimulation in toad's spinal cord. J. Neurophysiol. 18, 472–485 (1955).
Blackstad, T.W.: Commissural connections of the hippocampal region in the rat. with special reference to their mode of termination. J. comp. Neurol. 105, 417–538 (1956).
—: On the termination of some afferents to the hippocampus and fascia dentata. An experimental study in the rat. Acta anat. (Basel) 35, 202–214 (1958).
Blackstad, T.W.: Ultrastructural studies on the hippocampal region. Progr. Brain Res. 3, 122–148 (1963).
—: Mapping of experimental axon degeneration by electron microscopy of Golgi preparations. Z. Zellforsch. 67, 819–834 (1965).
—, and P.R. Flood: Ultrastructure of hippocampal axo-somatic synapses. Nature (Lond.) 198, 542–543 (1963).
-, and I. Foss: (1966). In preparation.
—, and A. Kjaerheim: Special axo-dendritic synapses in the hippocampal cortex. Electron and light microscopic studies on the layer of mossy fibers. J. comp. Neurol. 117, 133–159 (1961).
Cajal, S. Ramón y: Estructura del asta de Ammon. Anal. Soc. esp. Hist. Nat. Madr. 22, 53–114 (1893).
Caulfield, J.B.: Effects of varying the vehicle for OsO4 in tissue fixation. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 3, 827–830 (1957).
Eccles, J.C.: The control of neuronal activity by postsynaptic inhibitory action. Proc. XXIII Internat. Physiol. Congr., Tokyo, pp. 84–95 (1965).
—, R. Llinás, and K. Sasaki: Parallel fibre stimulation and the responses induced thereby in the Purkinje cells of the cerebellum. Exp. Br. Res. 1, 17–39 (1966).
Foss, I., and T.W. Blackstad: Reinvestigation of commissural fibers to regio superior (CA 1) of the rat hippocampus. J. Ultrastruct. Res. (1966). In press.
Fujita, Y., and H. Sakata: Electrophysiological properties of CA1 and CA2 apical dendrites of rabbit hippocampus. J. Neurophysiol. 25, 209–222 (1962).
Gray, E.G.: Axo-somatic and axo-dendritic synapses of the cerebral cortex. An electron microscope study. J. Anat. (Lond.) 93, 420–433 (1959).
Hamlyn, L.H.: The fine structure of the mossy fibre endings in the hippocampus of the rabbit. J. Anat. (Lond.) 96, 112–120 (1962).
—: An electron microscope study of pyramidal neurons in the Ammon's horn of the rabbit. J. Anat. (Lond.) 97, 189–201 (1963).
Kubota, K., H. Sakata, K. Takahashi and M. Uno: Location of the recurrent inhibitory synapse on cat pyramidal tract cell. Proc. Japan Acad. 41, 195–197 (1965).
Lorente de Nó, R.: Studies on the structure of the cerebral cortex. II. Continuation of the study of the Ammonic system. J. Psychol. Neurol. (Lpz.). 46, 113–177 (1934).
Millonig, G.: Further observations on a phosphate buffer for osmium solutions in fixation. In: Electron Microscopy. Fifth international congress for electron microscopy. P. P-8, Vol. I. Ed. S.S. Breese, Jr. New York and London: Academic Press 1962.
Nauta, W.J.H.: Über die sogenannte terminale Degeneration im Zentralnervensystem und ihre Darstellung durch Silberimprägnation. Schweiz. Arch. Neurol. Psychiat. 66, 353–376 (1950).
Reynolds, E.S.: The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J. Cell. Biol. 17, 208–212 (1963).
Westrum, L.E., and T.W. Blackstad: An electron microscopic study of the stratum radiatum of the rat hippocampus (regio superior, CA1) with particular emphasis on synaptology. J. comp. Neurol. 119, 281–309 (1962).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This investigation was supported by Public Health Service Research Grants NB 04764 and NB 02215, from the National Institute of Neurological Diseases and Blindness, which are gratefully acknowledged.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Andersen, P., Blackstad, T.W. & Lömo, T. Location and identification of excitatory synapses on hippoeampal pyramidal cells. Exp Brain Res 1, 236–248 (1966). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00234344
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00234344